Introduction
When we think of nutrition, we often focus on macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. However, micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are just as crucial for our well-being. Minerals are inorganic elements that our bodies need in varying amounts to support a range of physiological functions. From maintaining bone health to ensuring proper nerve signaling, minerals play an indispensable role in keeping us healthy.
For those following a plant-based diet, it is especially important to understand how to obtain adequate mineral intake, as some minerals are less bioavailable from plant sources than animal-based foods. This article explores why minerals are essential, their functions, recommended intake, and how to ensure sufficient consumption on a plant-based diet.
Why Does the Body Need Minerals?
Minerals are essential for numerous bodily functions, including:
- Bone and Teeth Strength – Minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium help build and maintain strong bones and teeth.
- Muscle Function – Magnesium and potassium regulate muscle contractions and prevent cramps.
- Blood Health – Iron and copper are critical for red blood cell production and oxygen transport.
- Nervous System Support – Sodium, potassium, and calcium help nerve cells communicate.
- Hormone Production – Iodine is vital for thyroid hormone function, which controls metabolism.
- Fluid Balance – Sodium, potassium, and chloride help regulate water balance in the body.
- Immune Function – Zinc and selenium support immune defense and antioxidant activity.
Since the body cannot produce minerals on its own, we must obtain them from our diet. Let’s explore the key minerals, their functions, recommended intake, and plant-based sources.
Essential Minerals and Their Functions
Macrominerals (Needed in Larger Amounts)
- Calcium
- Function: Supports bone and teeth health, muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and blood clotting.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 1000–1300 mg (varies by age and gender).
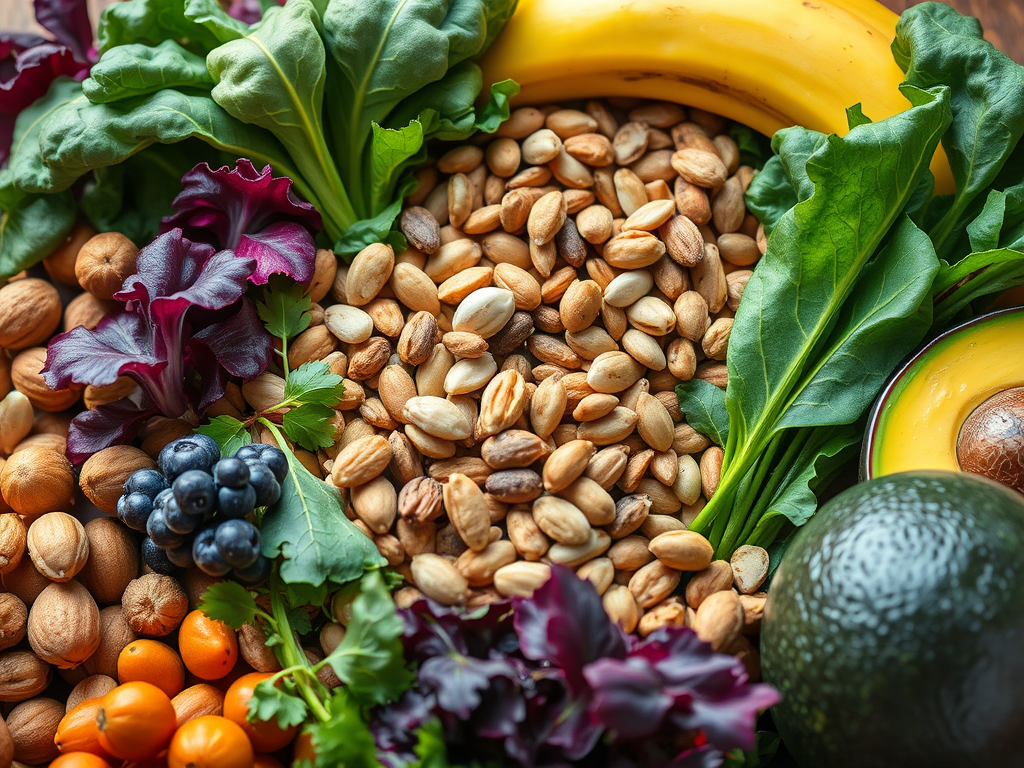
- Plant-Based Sources: Fortified plant milk, tofu (calcium-set), leafy greens (kale, bok choy), sesame seeds, almonds.
- Magnesium
- Function: Regulates muscle and nerve function, supports energy production, and helps with bone formation.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 310–420 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds (pumpkin, chia), whole grains, leafy greens, bananas.
- Potassium
- Function: Maintains fluid balance, supports nerve signaling and muscle contraction, and helps control blood pressure.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 2600–3400 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Bananas, sweet potatoes, beans, lentils, avocados, spinach, oranges.
- Phosphorus
- Function: Supports bone and teeth health, energy production, and cell repair.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 700 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Nuts, seeds, beans, whole grains.
- Sodium
- Function: Helps maintain fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions.
- Recommended Daily Intake: Less than 2300 mg (excessive intake can lead to high blood pressure).
- Plant-Based Sources: Naturally present in celery, beets, and seaweed, though most sodium comes from processed foods.
- Chloride
- Function: Maintains fluid balance and aids digestion by forming stomach acid.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 1800–2300 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Seaweed, tomatoes, olives, celery.
Trace Minerals (Needed in Smaller Amounts)
- Iron
- Function: Essential for oxygen transport in blood, energy production, and immune function.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 8–18 mg (higher for menstruating persons).
- Plant-Based Sources: Lentils, chickpeas, tofu, quinoa, dark leafy greens, fortified cereals.
- Absorption Tip: Iron from plant sources (non-heme iron) is less bioavailable; consuming it with vitamin C (e.g., citrus fruits, bell peppers) enhances absorption.
- Zinc
- Function: Supports immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 8–11 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Seeds (pumpkin, hemp, sesame), nuts, whole grains, legumes.
- Absorption Tip: Soaking and sprouting grains and legumes can improve zinc absorption.
- Copper
- Function: Assists in iron absorption, red blood cell production, and immune function.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 0.9 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Nuts, seeds, whole grains, dark chocolate, mushrooms.
- Iodine
- Function: Critical for thyroid hormone production, which regulates metabolism.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 150 mcg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Seaweed, iodized salt, potatoes.
- Selenium
- Function: Powerful antioxidant, supports thyroid health and immune function.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 55 mcg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Brazil nuts (one nut can provide the full daily requirement), sunflower seeds, mushrooms.
- Manganese
- Function: Supports bone health, metabolism, and antioxidant function.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 1.8–2.3 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Whole grains, nuts, leafy greens, pineapple.
- Fluoride
- Function: Helps with dental and bone health.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 3–4 mg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Water (if fluoridated), tea, spinach.
- Molybdenum
- Function: Supports enzyme function in detoxification.
- Recommended Daily Intake: 45 mcg.
- Plant-Based Sources: Legumes, whole grains, nuts.
Maximizing Mineral Absorption on a Plant-Based Diet
While a plant-based diet can provide all essential minerals, absorption can sometimes be hindered by plant compounds such as phytates and oxalates. Here are some strategies to optimize mineral intake:
- Pairing Nutrients: Vitamin C enhances iron absorption; consuming calcium and magnesium together supports bone health.
- Soaking and Sprouting: Reduces phytates in grains, nuts, and legumes, improving mineral absorption.
- Fermenting Foods: Increases bioavailability of minerals in plant-based foods.
- Diversifying Food Sources: Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods ensures adequate intake of essential minerals.
Conclusion: Are You Getting Enough Minerals?
Minerals are often overlooked in dietary discussions, yet they play a crucial role in our health. Whether you follow a plant-based diet or not, ensuring sufficient mineral intake is key to optimal well-being.
Now, I’d love to hear from you!
- Have you ever struggled with getting enough minerals on a plant-based diet?
- Do you have any favorite plant-based sources of essential minerals?
- What strategies do you use to enhance mineral absorption in your diet?
Drop your thoughts in the comments below, and let’s keep the conversation going!

Leave a comment